Raw water tanks, an essential component in a variety of industrial and residential systems, have gained increasing attention in discussions about water management and conservation. These tanks are used to store untreated water that will eventually be processed for various uses, ranging from industrial applications to potable water in households. A deep dive into their advantages, types, maintenance, and best practices can provide valuable insights for both consumers and professionals in the industry.

At the heart of numerous industrial processes, raw water tanks serve as a primary storage solution. They are typically crafted from materials like polyethylene, stainless steel, and fiberglass, each offering distinct benefits in terms of durability and resistance to environmental factors. Polyethylene tanks are favored for their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, making them ideal for quick installations and situations where mobility is necessary. Conversely, stainless steel tanks are renowned for their robustness and longevity, often employed in industries where the stored water might cause corrosion in lesser materials.
The choice of raw water tank should align with its intended application.
For instance, in agricultural settings, where large volumes of water are required for irrigation, having a tank with ample capacity is crucial. Here, fiberglass tanks might come into play due to their balance of durability and ease of installation. Moreover, in urban areas, where space might be a constraint, vertical tanks can maximize storage without requiring a large footprint.
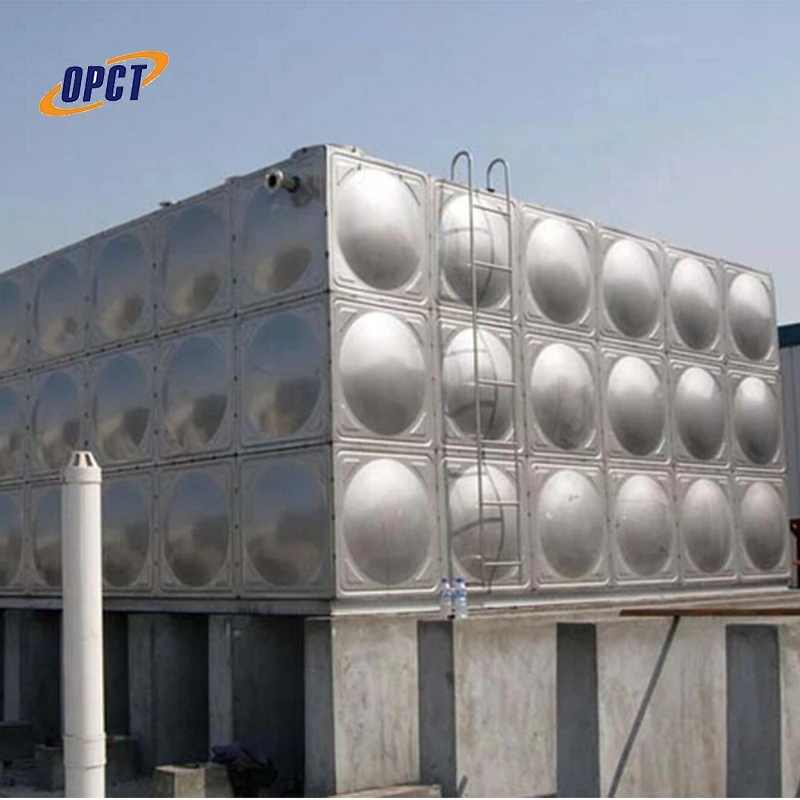

Proper maintenance of raw water tanks is vital to ensure their longevity and efficiency. Regular inspections to check for leaks, sediment build-up, and integrity of the tank material can prevent significant issues and extend the tank's operational life. Implementing a scheduled cleaning regimen helps in maintaining the quality of stored water and supports the tank’s structural health.
raw water tank
Advanced features in modern raw water tanks further enhance their functionality. For instance, integrating filtration systems at the tank inlet can prevent large particles and impurities from entering, thus preserving water quality. Moreover, automated monitoring systems equipped with level sensors can alert operators to fluctuations in water volume, helping in efficient water management and preventing overflow or unnecessary wastage.
Security is another concern when managing raw water tanks, particularly in regions prone to tampering or contamination risks. Securing the tank with lockable lids and ensuring that it is installed in a secure location can mitigate such threats. Additionally, regular water quality tests are advisable to assure that there has been no contamination, thereby safeguarding downstream water usage.
As global focus shifts towards sustainable practices, the role of raw water tanks becomes even more pivotal. Their integration into rainwater harvesting systems exemplifies an effective strategy to augment water availability while reducing reliance on municipal sources. Such applications not only support environmental conservation but also offer economic benefits by lowering water costs in the long run.
In conclusion, raw water tanks are a versatile solution for addressing various water storage needs. Understanding their diverse applications, maintenance requirements, and enhancement options empowers users to make informed decisions and optimize water resources efficiently. Whether for industrial applications or residential use, these tanks provide a fundamental resource management tool that aligns with both current challenges and future sustainability goals. Combining traditional practices with innovative technologies will undoubtedly enhance their role in modern water management systems.