

Understanding Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Grating A Comprehensive Overview
Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP) grating has emerged as a revolutionary material in various engineering applications, providing a robust solution for environments that demand both strength and lightweight properties. This technology merges the essential features of traditional materials with modern advancements, leading to enhanced performance characteristics beneficial in numerous sectors including construction, marine, and chemical industries.
Introduction to FRP Grating
FRP grating is composed of a polymer matrix reinforced with fibers, commonly glass, carbon, or aramid fibers. This combination not only amplifies strength but also contributes to the grating's resilience against environmental degradation. Unlike conventional materials like steel or wood, FRP grating is designed to resist corrosion, making it an ideal choice for harsh conditions where moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation are prevalent.
Key Features and Benefits
1. Corrosion Resistance One of the standout features of FRP grating is its ability to withstand corrosive elements, which is particularly valuable in industries such as wastewater treatment, chemicals, and pulp and paper. This resistance leads to lower maintenance costs and longer service life compared to traditional metal gratings.
2. Lightweight Nature FRP grating is significantly lighter than steel, facilitating easier handling and installation. The reduced weight can also contribute to lower transportation costs and expedited construction timelines, making it a practical option for various applications.
3. High Strength-to-Weight Ratio Despite being lightweight, FRP grating boasts a high strength-to-weight ratio. This means it can bear substantial loads while maintaining its structural integrity, making it suitable for pedestrian walkways, platforms, and industrial flooring.
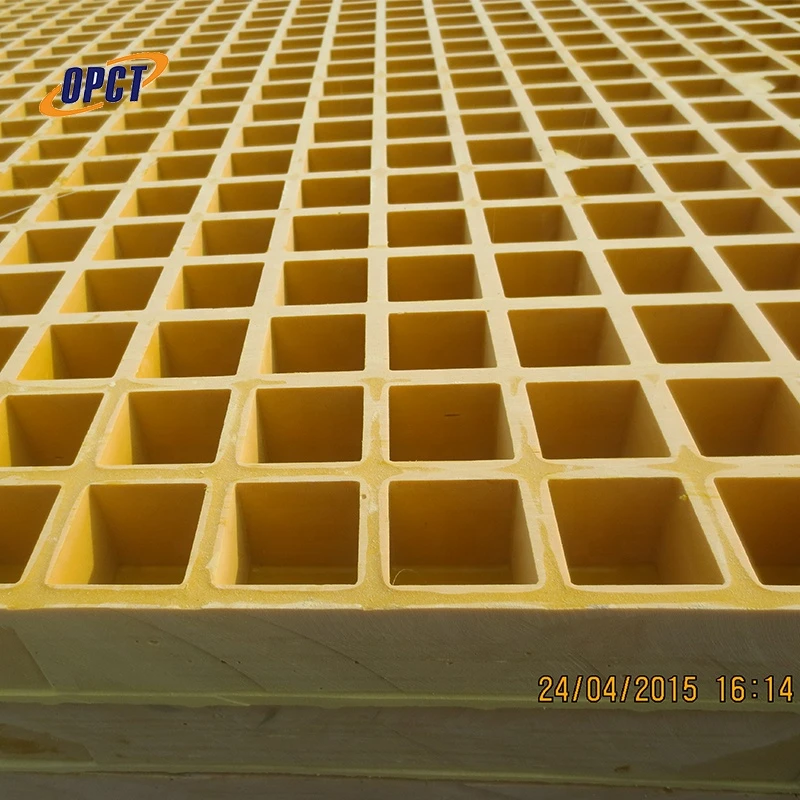

4. Customization and Versatility FRP grating can be manufactured in different colors, sizes, and forms to meet specific project requirements. This versatility allows it to seamlessly integrate into any design scheme while providing essential functional benefits. Its non-slip surface can also be tailored to enhance safety in slippery environments.
5. Thermal and Electrical Insulation Unlike metal counterparts, FRP grating is a poor conductor of heat and electricity, which makes it an excellent choice for applications in electrical substations and in areas requiring thermal insulation.
Applications of FRP Grating
Given its myriad advantages, FRP grating is utilized across numerous fields. In the chemical industry, for instance, it is employed for platforms, walkways, and staircases where chemical exposure is a concern. The construction sector benefits from FRP grating in bridge decks, flooring systems, and even architectural applications due to its aesthetic appeal in various colors and designs.
In marine environments, FRP grating can be found on docks, piers, and ship decks where resistance to saltwater and corrosion is paramount. Furthermore, the oil and gas industry employs FRP grating for offshore platforms and refineries, enhancing safety and longevity in challenging conditions.
Conclusion
In summary, Fiber Reinforced Polymer grating represents a significant advancement in engineering materials, merging desirable properties such as corrosion resistance, lightweight performance, and customizable options. Its applications across various industries underscore its importance and versatility. As demands for sustainable and durable materials continue to rise, FRP grating is poised to play an increasingly vital role in future infrastructure and industrial projects, offering solutions that stand up to the challenges of modern engineering and environmental sustainability. By investing in FRP technologies, industries can benefit from enhanced safety, reduced maintenance costs, and a commitment to quality that prioritizes longevity and performance.